Digital Civic Engagement as an Equity Solution for Cities & Counties
.png)
Zencity
The Platform for Community Trust
Social media has the power to positively impact civic engagement. It is an opportunity for local governments to increase engagement, to get more equitable community feedback and reach more residents, and to help build trust with the community by more easily meeting them where they are. Today’s blog takes you through both the challenges and the successes of social media’s impact on civic engagement and why it has so much to offer local government.
Traditionally, civic engagement has meant in-person involvement in your local community. If you were engaged civically, you attended city council meetings, voted, took an active role in civic organizations, or helped to establish community organizations. Most of this was outside the home and involved a small, homogenous, group of people. On rare occasion – perhaps once every year or two – a resident satisfaction survey by telephone to snail-mail provided the opportunity to engage “remotely.”
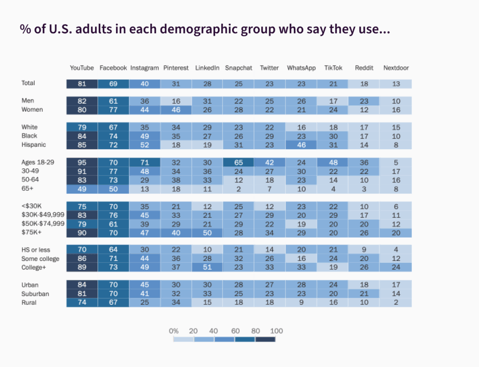
Today, leveraging social media for civic engagement is a must. Whether it’s Facebook, Twitter, Snapchat, Instagram, Nextdoor, or YouTube, civic engagement is now taking place online. Social media pervades every aspect of our lives: for youth aged 18-29, 84% use social media sites and a majority of users over 50 (73%) are also on one of the different platforms.
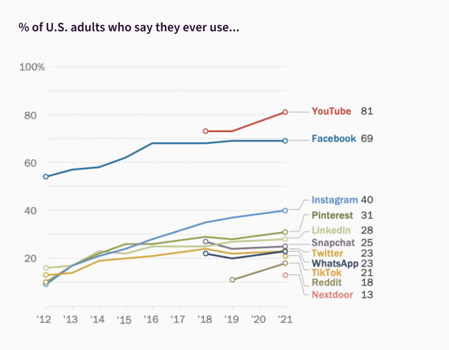
What does this mean for civic engagement? Civic engagement no longer stops at the door of your residents’ homes. It’s a possibility 24/7. It’s accessible to a broad and diverse audience who can engage or participate whenever, and wherever they are, and about whichever topic or issue they choose.
Even in 2018, before the pandemic, roughly half of Americans said they were civically active on social media. They had taken part in an online community group, shared a hashtag, looked up information on local events, initiatives, or rallies, and encouraged people to support a certain topic or issue.
Since then, social media use has only grown, and along with it, the impact of social media on civic engagement. Once COVID-19 hit, it was not a matter of online or offline but remote civic engagement, and one of the key players in that scenario was and remains social media – digital civic engagement.
What is digital civic engagement?
Digital civic engagement is the “new normal” for civic engagement and civic activities of all kinds. Digital civic engagement brings people to a cause or a project via social media or online portal. The arena for civic engagement has widened to include more people and not just the squeaky wheels.
Civic engagement is inseparable from the digital media landscape, and research suggests that older frames which view the ‘online’ and ‘offline’ as entirely separate experience are inaccurate . . .
According to a Unicef analysis, there is no offline or online for today’s youth: “Civic engagement is inseparable from the digital media landscape, and research suggests that older frames which view the ‘online’ and ‘offline’ as entirely separate experiences are inaccurate for today’s youth.” The report goes on to explain that digital media today includes “a degree of agency previously unexperienced, together with the ease for an ‘audience’ to author, remix and remake popular culture themselves.” And, as we all know, digital media, from the absurd to the sublime, has the potential to go viral and impact every corner of the globe.
Can social media improve civic engagement?
Social media can even the playing field in civic engagement. It helps to lower the barriers to civic participation resulting in a variety of advantages:
- Diversity One of the biggest ways that social media improves civic engagement is in opening opportunities for more people to participate. Under-served and marginalized communities, such as the LGBTQIA+ community have found homes online through groups on social media or with like minded individuals. These once silent minorities now have a place to be heard and can participate in local government through online civic engagement. Additionally, groups that historically have felt uncomfortable with or distrusting of government may feel more comfortable in a place they’re already used to – their own social media platform rather than inside city hall.
- Relatability One way to keep residents involved in civic life is to make it relatable and maybe, even fun! Social media allows cities and counties to engage with residents on both serious and everyday topics. Less formal communications on official social media channels empowers usually silent voices to engage in a non-threatening way. To encourage correct parking of scooters, the City of Orlando tweeted a picture of a car parked partly on the sidewalk and partly on the street. They also like to post pictures of their famous swans at Lake Eola. Digital civic engagement provides an opportunity for a local government organization to add personality, branding, and a voice to local leaders beyond press conferences and town hall meetings.
- Accessibility More than 79% of the U.S. population owns a smartphone and that is all they need to begin or continue their civic engagement. Meeting residents online means meeting them where they are which lowers the barriers to participation in local government tremendously. Digital civic engagement also removes restrictions of time and place and enables engagement in multiple languages much more easily. By logging in to their own Facebook account, a mobile city app, or their Twitter feed, residents can immediately see what is happening in their neighborhood, comment on something the official city or county has posted, and check for news on the issues that are them.
Social media and civic engagement: The challenges
Even though digital civic engagement provides a wealth of opportunity and can help solve for equity in local governance, it does not come without its challenges. Social media in America is an expression of free speech. On the plus side, understanding resident needs from sentiment on social media can help local governments plan strategically and respond to immediate concerns but, local governments must also ensure that free speech is not stifled on social media by some of the more challenging aspects of the platforms nor that social media becomes a source of misinformation or a detrimental force in the community.
- Offensive & Hateful Language On the negative side, it is easy for bigoted and threatening speech to raise its ugly head and to be shared widely through social media channels. It is difficult for social media platforms to monitor hate speech that turns up in both comments and other forms. Local residents who encounter hate speech or racism or marginalization of others may not engage online. They will simply turn away and stay away to avoid abuse, especially if they find this kind of speech in local, neighorhood, or community groups, or in discourse on official channels, for example in the comment sections of official posts.
- Misinformation Video and posts on social media also have the ability to spread misinformation and/or false claims. In this case, social media can be harmful with residents interacting and relying on information that may not be true or may be misleading. This makes it challenging for local governments to build trust and transparency when residents can’t tell fact from fiction. On a plus, leveraging social media in digital civic engagement is also a great platform for local governments to widely disseminate correct information and own the narrative – or to nip misinformation in the bud.
- Online interaction Another issue which makes social media and civic engagement tricky is the loss of face to face interactions. Without facial cues or in lieu of a real conversation, it’s difficult to understand the tone of social media posts and comments. The misinterpretations that can arise can be another barrier to creating real digital civic engagement.
Even with all these challenges, the truth is that social media and civic engagement are a match. Read on to see the benefits and how we can use social media to improve civic engagement.
What is social participation and how can it be used by local governments?
Social participation is civic engagement through social media – and there is a big opportunity for government in this kind of participation. In fact, according to our own Zencity study, 87% of overall social media interactions that provided input on local government services and experiences came from unofficial sources, and only 13% came from local government-managed pages. Social participation is happening but cities and counties are missing out on the information they don’t see on their official channels.
Apache Junction, AZ, is a city in the Phoenix metropolitan area, one of the fastest-growing areas in the U.S. The announcement of the sale of a large parcel of land adjacent to the City, immediately created an uproar in Apache Junction. In a proactive step, and to listen to residents online, Apache Junction used the Zencity dashboard to monitor sentiment around the land sale. 80% of the discourse about the topic registered as negative!
The citizens needed more information to understand exactly what was happening so the City took to social media to assuage resident concerns and even created a video that clarified information about the sale and specifically addressed the top concerns raised by community members that had been shared on social media.
The City then measured the video’s impact on community dialogue using Zencity data. In fact, not only did the video itself receive good feedback, overall there was a drop in discourse about the land sale and a major shift in sentiment.
By acknowledging the social media impact on civic participation, Apache Junction quickly and successfully listened to residents’ opinions, adjusted their messaging and continued building trust with the community.
Zencity takes civic engagement a step further, and meets residents where they spend time: online. Through a mix of cutting-edge AI and expert analysis, Zencity aggregates organic discourse through unofficial online channels – such as social media – to identify trending topics and keywords within individual jurisdictions, and assess positive or negative resident sentiment around those subjects. We pair this with digital online surveys – both topical polls and ongoing resident satisfaction surveys, and direct engagement opportunities. This allows local governments to gain a better understanding of what is most important to all residents, not just the squeaky wheels that make their voices heard, and what services residents may be more or less satisfied with, in real-time and over time.
%20copy-1.png?width=544&height=120&name=Logo_black%20(1)%20copy-1.png)



